오버피팅 (Overfitting)
If there exists a model with estimated parameters w' such that
1) training error (w.hat) < training error (w')
2) true error (w.hat) > true error (w')
trainint set에는 매우 잘 맞는데 don't generalize well
Training/Test Split
Training Set / Test Set에 각각 얼마나 분배할 것인가?
1) Training set에 너무 적게 넣는다면 -> W 잘 안 나옴
2) Test set에 너무 적게 넣는다면 -> 일반화 잘 안 됨
완벽한 공식은 없다.
일반화하기 위한 적당한 양의 데이터를 test set에 넣어야 한다.
이렇게 해서 training에 너무 적은 양이 남는다면, cross validation과 같은 다른 방법도 있다.
3 Sources of Error
Noise, Bias, Variance
1. Noise
Data are inherently noisy.
variance in house price
Irreducible error -> better model을 고른다고 줄일 수 없다
우리가 컨트롤 할 수 있는 건 bias, variance
2. Bias
True relation between x and y
difference between average fit and true function.
is our model flexible enough?
3. Variance
how different can my specific fits to a given data set be from one another
low complexity -> low variance
how much can the fits vary
erratic predictions
high complexity models -> high variance, low bias
Bias - Variance Tradeoff
MSE (Mean Squared Error) = Bias^2 + Variance
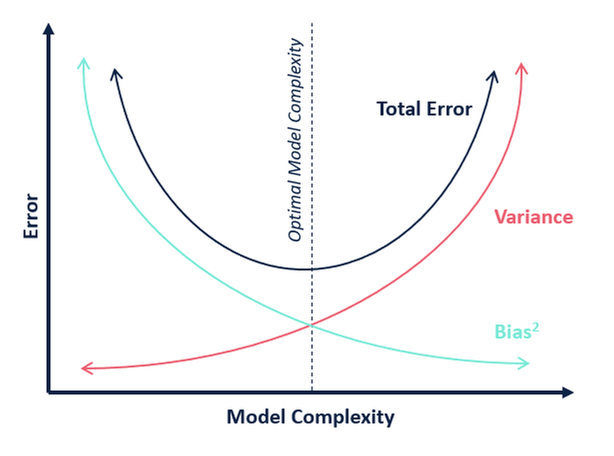
find the sweet spot
Just like with generalization error, we cannot compute bias and variance.
why?
bias, variance가 true function과의 관계로 정의됨
Size가 n인 모든 가능한 데이터셋을 평균내야 하는데 그게 뭔지 모르기 때문
Error vs. amount of data
for a fixed model complexity
The Regression / ML Work flow
1. Model selection
2. Model assessment
Hypothetical implementation
Training set / Test set
1. Model Selection
For each considered model complexity λ :
1) Estimate parameters W on training data
2) Assess performance of W on test data
3) Choose λ* to be λ with lowest test error
2. Model assessment
compute test error of W (fitted model for selected complexity λ*) to approx. generalization error
Test set -> Validation set + Test set
'Data Science > Machine Learning' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 머신러닝 (Machine Learning) (0) | 2023.05.21 |
|---|---|
| [2주차] Multiple Regression (0) | 2021.05.27 |
| [1주차] Coursera Machine Learning : Regression (0) | 2021.05.27 |
| Scikit-Learn을 이용한 머신러닝 (0) | 2020.10.21 |
| 머신러닝 기본 (0) | 2020.08.04 |
